Spring Boot + MyBatis 프로젝트 연습 목록
- 01. 신규 Spring Boot 프로젝트 만들기
- 02. Thymeleaf, spring-boot-devtools 추가
- 03. Spring Boot에 H2 추가
- 04. Spring Boot + H2 + Jdbc로 사용해보기 (현재 포스트)
현재 포스팅하는 시리즈는 Spring Boot와 MyBatis를 결합한 프로젝트를 연습하는 부분입니다. 하지만 이번 포스팅은 MyBatis를 설정하기 전에 먼저 Jdbc로 사용하는 방법을 확인하고 싶어 진행한 곁가지입니다. 01~03번 포스팅까지는 동일하게 진행되고 사용함에 있어 04.Jdbc / 05.MyBatis(이후 정리 예정) 이렇게 나뉘어집니다.
JDBC 사용하기
1. pom.xml에 아래 내용 추가 (앞선 포스팅 H2 설정하기에서 이미 추가하였다)
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2. account 테이블 생성 및 데이터 입력
: schema.sql 내용 변경 (이전에는 h2 설정이 잘 되었는지 확인하기 위한 테스트 테이블 생성이 들어있었다.)
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS accounts;
CREATE TABLE accounts (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
email VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL
);
INSERT INTO accounts (email) VALUES
('email1@email.com'),
('email2@email.com'),
('email3@email.com');
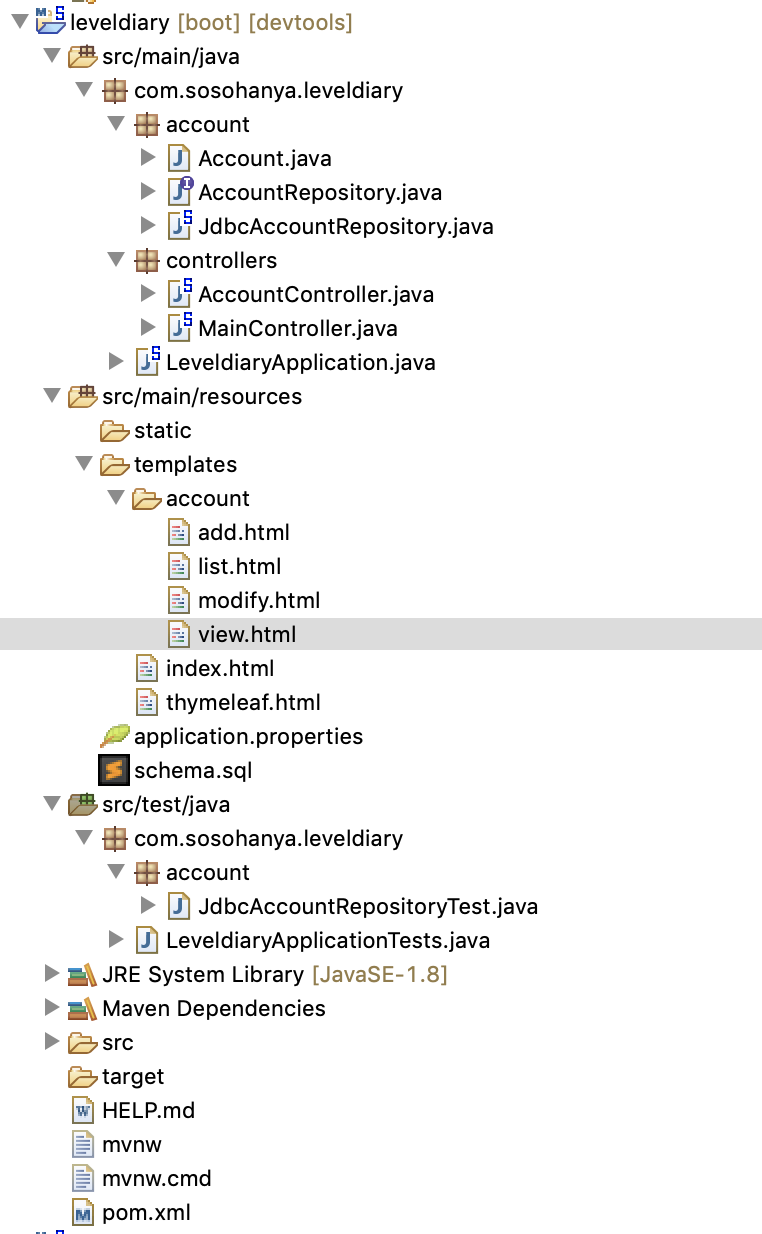
3. Account 도메인 객체 생성
: /src/main/java 하위에 com.sosohanya.leveldiary.account 패키지를 만들고 Account 클래스 생성
(패키지 및 파일 구조는 본인이 선호하는 바에 따라)
package com.sosohanya.leveldiary.account;
public class Account {
private long id;
private String email;
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public Account(long id, String email) {
this.id = id;
this.email = email;
}
public Account(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account [id=" + id + ", email=" + email + "]";
}
}
4. 데이터 처리 인터페이스 정의
: /src/main/java 하위에 com.sosohanya.leveldiary.account 패키지에 AccountRepository 인터페이스 생성
(인터페이스를 사용하지 않고 바로 클래스로 구현할 수도 있겠지만..나중을 위해서 그러지 않겠습니다. 인터페이스(Interface) 개념을 간단히 잘 소개한 생활코딩-인터페이스 페이지 보기 [새창])
AccountRepository.java
package com.sosohanya.leveldiary.account;
import java.util.List;
public interface AccountRepository {
int count();
long save(Account account);
int update(Account account);
int deleteById(Long id);
void deleteAll();
List<Account> findAll();
Account findById(Long id);
Account findByEmail(String email);
}
5. 데이터 처리 구현
: /src/main/java 하위에 com.sosohanya.leveldiary.account 패키지에 AccountRepository를 구현하는 JdbcAccountRepository 클래스 생성
JdbcAccountRepository.java 소스
package com.sosohanya.leveldiary.account;
//... import 구문 생략 ...
@Repository
public class JdbcAccountRepository implements AccountRepository {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Override
public int count() {
return jdbcTemplate
.queryForObject("select count(*) from accounts", Integer.class);
}
@Override
public long save(Account account) {
//자동 생성되는 키 리턴받기
KeyHolder keyHolder = new GeneratedKeyHolder();
jdbcTemplate.update(connection -> {
PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement("insert into accounts (email) values (?)", Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
ps.setString(1, account.getEmail());
return ps;
}, keyHolder);
return (long)keyHolder.getKey();
//자동 생성되는 키를 받을 수 없다. 성공 또는 실패. 0 또는 1만 반환
//return jdbcTemplate.update("insert into accounts (email) values (?)",
// account.getEmail());
}
@Override
public int update(Account account) {
return jdbcTemplate.update("update accounts set email = ? where id = ?",
account.getEmail(),
account.getId());
}
@Override
public int deleteById(Long id) {
return jdbcTemplate.update("delete accounts where id = ?",
id);
}
@Override
public List<Account> findAll() {
return jdbcTemplate.query("select * from accounts",
(rs, rowNum) -> new Account(
rs.getLong("id"),
rs.getString("email")
)
);
}
@Override
public Account findById(Long id) {
try {
return jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select * from accounts where id = ?",
new Object[] {id},
(rs, rowNum) -> Optional.of(new Account(
rs.getLong("id"),
rs.getString("email")
))
).orElse(null);
}catch(EmptyResultDataAccessException e) {
return null;
}
}
@Override
public Account findByEmail(String email) {
try {
return jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select * from accounts where email = ?",
new Object[] {email},
(rs, rowNum) -> Optional.of(new Account(
rs.getLong("id"),
rs.getString("email")
))
).orElse(null);
}catch(EmptyResultDataAccessException e) {
return null;
}
}
@Override
public void deleteAll() {
jdbcTemplate.update("delete from accounts");
}
}
6. 단위 테스트로 확인 : 생성한 JdbcAccountRepository에 대한 테스트 작성 및 테스트
(부끄럽지만 실무를 하면서 단위 테스트를 적용해본적이 없어 아래 단위 테스트 내용은 단위 테스트 생초보의 작성내용이라는 점 감안해주시길 바랍니다. 저는 Java 생초보, 단위 테스트 생초보. 저는 여러 가지로 게으른 개발자였습니다. ㅠㅠ)
JdbcAccountRepositoryTest.java 소스
package com.sosohanya.leveldiary.account;
//... import 구문 생략 ...
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class JdbcAccountRepositoryTest {
@Autowired
JdbcAccountRepository jdbcAccountRepository;
String defaultEmail = "add@email.com";
@Before
public void setUp() {
jdbcAccountRepository.deleteAll();
}
@Test
public void count() {
assertEquals(0, jdbcAccountRepository.count());
jdbcAccountRepository.save(new Account("add1@email.com"));
jdbcAccountRepository.save(new Account("add2@email.com"));
jdbcAccountRepository.save(new Account("add3@email.com"));
assertEquals(3, jdbcAccountRepository.count());
}
@Test
public void saveAndFindAll() {
jdbcAccountRepository.save(new Account("add1@email.com"));
jdbcAccountRepository.save(new Account("add2@email.com"));
jdbcAccountRepository.save(new Account("add3@email.com"));
List<Account> getAll = jdbcAccountRepository.findAll();
assertEquals(3, getAll.size());
}
@Test
public void saveAndFindById() {
long resultId = jdbcAccountRepository.save(new Account(defaultEmail));
Account getAccount = jdbcAccountRepository.findById(resultId);
assertNotNull(getAccount);
assertEquals(defaultEmail, getAccount.getEmail());
}
@Test
public void saveAndFindByEmail() {
jdbcAccountRepository.save(new Account(defaultEmail));
Account getAccount = jdbcAccountRepository.findByEmail(defaultEmail);
assertNotNull(getAccount);
assertEquals(defaultEmail, getAccount.getEmail());
}
@Test
public void update() {
long resultId = jdbcAccountRepository.save(new Account(defaultEmail));
Account getAccount = jdbcAccountRepository.findById(resultId);
getAccount.setEmail("update@email.com");
jdbcAccountRepository.update(getAccount);
Account updatedAccount = jdbcAccountRepository.findById(resultId);
assertEquals("update@email.com", updatedAccount.getEmail());
}
@Test
public void deleteById() {
long resultId1 = jdbcAccountRepository.save(new Account("add1@email.com"));
long resultId2 = jdbcAccountRepository.save(new Account("add2@email.com"));
long resultId3 = jdbcAccountRepository.save(new Account("add3@email.com"));
jdbcAccountRepository.deleteById(resultId2);
assertEquals(2, jdbcAccountRepository.count());
assertNotNull(jdbcAccountRepository.findById(resultId1));
assertNull(jdbcAccountRepository.findById(resultId2));
assertNotNull(jdbcAccountRepository.findById(resultId3));
}
}- 오류 발생 : org.h2.jdbc.JdbcSQLNonTransientConnectionException: Database may be already in use: null. Possible solutions: close all other connection(s);
- 로컬 서버가 실행된 상태에서 JUnit test를 실행할 때 나온 현상. (이미 로컬 서버에서 Database를 사용중이라 생긴 문제로 파악됨)
- 해결 : application.properties 파일에서 spring.datasource.url 속성에 ;AUTO_SERVER=TRUE 내용 추가
- AUTO_SERVER=TRUE
: 서버를 수동으로 시작하지 않고도 여러 프로세스가 동일한 데이터베이스에 액세스 가능. 데이터베이스가 이미 열려있는지 여부에 관계없이 동일한 데이터베이스 URL 사용이 가능. (이 기능은 in-memory 데이터베이스에서는 작동하지 않음) 자세한 내용은 H2 공식 웹사이트 - Features : Automatic Mixed Mode 확인 [새창]
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:~/leveldiary;AUTO_SERVER=TRUE
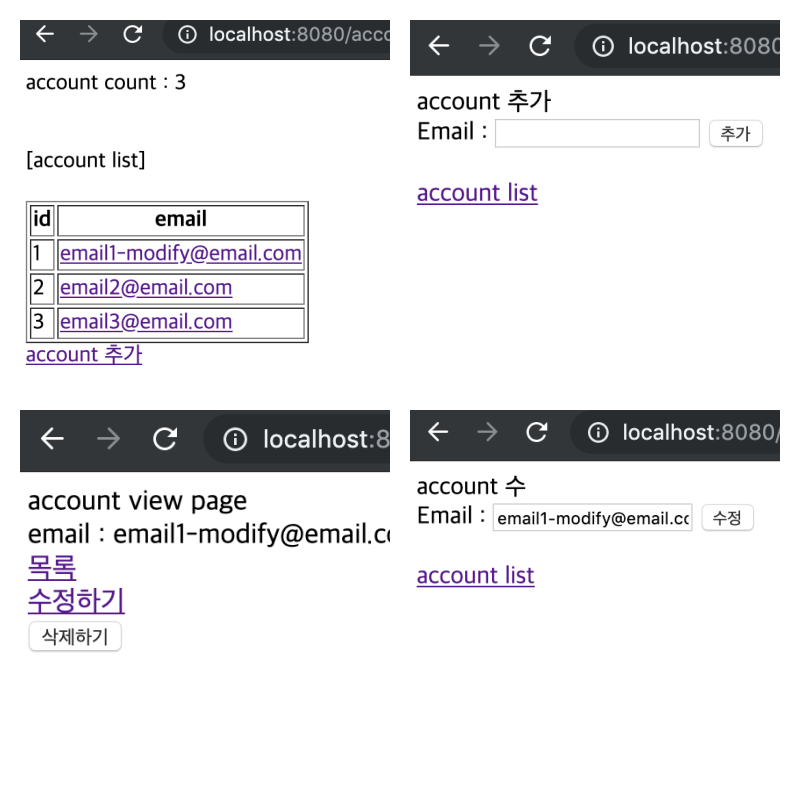
7. 위에서 생성한 JdbcAccountRepository를 사용하는 목록/내용보기/추가/수정/삭제 기능을 간단하게 구현
(프로젝트를 만들어보고 돌아가는 것을 보기 위한 것이기에 디자인적인 부분은 전혀 없습니다. )
7-1. AccountController.java 생성 (/scr/main/java 폴더내의 com.sosohanya.leveldiary.controllers)
package com.sosohanya.leveldiary.controllers;
//... import 구문 생략 ...
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/account")
public class AccountController {
@Autowired
JdbcAccountRepository jdbcAccountRepository;
@GetMapping("/list") //목록
public String list(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("accounts", jdbcAccountRepository.findAll());
model.addAttribute("count", jdbcAccountRepository.count());
return "account/list";
}
@GetMapping("/add") //추가 Form
public String add() {
return "account/add";
}
@PostMapping("/add") //추가 처리
public String addProcess(String email){
jdbcAccountRepository.save(new Account(email));
return "redirect:/account/list";
}
@GetMapping("/{id}") //상세보기
public String view(@PathVariable Long id, Model model) {
model.addAttribute("account", jdbcAccountRepository.findById(id));
return "account/view";
}
@GetMapping("/{id}/modify") //수정 Form
public String modify(@PathVariable Long id, Model model) {
model.addAttribute("account", jdbcAccountRepository.findById(id));
return "account/modify";
}
@PostMapping("/{id}/modify") //수정 처리
public String modifyProcess(@PathVariable Long id, String email) {
Account account = jdbcAccountRepository.findById(id);
account.setEmail(email);
jdbcAccountRepository.update(account);
return String.format("redirect:/account/%d", id) ;
}
@PostMapping("/{id}/delete") //삭제 처리
public String deleteProcess(@PathVariable Long id) {
jdbcAccountRepository.deleteById(id);
return "redirect:/account/list";
}
}7-2. src/main/resources/templates/account 폴더 생성 후 해당 폴더에 list.html / add.html / view.html / modify.html 파일 생성 (thymeleaf 템플릿을 사용)
- list.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.com"> <!-- xmlns:th를 설정하지 않으면 에디터에서 경고가 표시되어 신경쓰임 -->
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
account count : <span th:text="${count}"></span>
</div>
<br/><br/>
<div>[account list]</div><br/>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>id</th>
<th>email</th>
</tr>
<tr th:each="account : ${accounts}">
<td th:text="${account.id}"></td>
<td><a href="/account/1" th:href="@{/account/{id}(id=${account.id})}" th:text="${account.email}"></a></td>
</tr>
</table>
<a th:href="@{/account/add}" href="/account/add">account 추가</a>
</body>
</html>- add.html
...생략...
<form method="post" th:action="@{/account/add}">
Email : <input type="text" name="email" />
<button type="submit">추가</button>
</form>
<br/>
<a href="/account/list" th:href="@{/account/list}">account list</a>
...생략...- view.html
...생략...
<div>
email : <span th:text="${account.email}"></span>
</div>
<div>
<a href="/account/list" th:href="@{/account/list}">목록</a> <br/>
<a href="/account/1/modify" th:href="@{/account/{id}/modify(id=${account.id})}">수정하기</a> <br/>
<form method="post" th:action="@{/account/{id}/delete(id=${account.id})}">
<button type="submit">삭제하기</button>
</form>
</div>
...생략...- modify.html
...생략...
<form method="post" th:action="@{/account/{id}/modify(id=${account.id})}">
Email : <input type="text" name="email" th:value="${account.email}" />
<button type="submit">수정</button>
</form>
<br/>
<a href="/account/list" th:href="@{/account/list}">account list</a>
...생략...
지금까지의 내용은 github에 branch:004-using-jdbc[새창]로 확인하실 수 있습니다
참고 사이트 :
- Spring 공식사이트 - Accessing Relational Data using JDBC with Spring
- Mkyong.com - Spring Boot JDBC Examples
Spring Boot + MyBatis 프로젝트 연습 목록
- 01. 신규 Spring Boot 프로젝트 만들기
- 02. Thymeleaf, spring-boot-devtools 추가
- 03. Spring Boot에 H2 추가
- 04. Spring Boot + H2 + Jdbc (현재 포스트)
'냐냐한 IT > 냐냐한 Spring Boot' 카테고리의 다른 글
| MyBatis Logging 추가 (0) | 2019.09.25 |
|---|---|
| Spring Boot + H2 + MyBatis로 사용해보기 (0) | 2019.09.22 |
| Spring Boot에 H2 추가 (0) | 2019.09.16 |
| Thymeleaf, spring-boot-devtools 추가 (0) | 2019.09.14 |
| 신규 Spring Boot 프로젝트 만들기 (2) | 2019.09.12 |